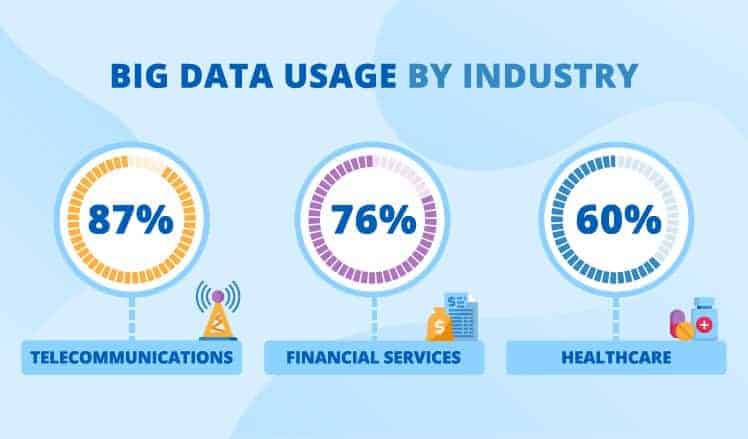
Many companies have also reported significant challenges when implementing big data analytics initiatives.
Talent Acquisition. Data scientists and big data experts are high in demand —and highly paid — workers in the IT field. The AtScale survey found that the lack of a big data skillset has been the number one big data challenge. Hiring or training staff can increase costs considerably, and the process of acquiring big data skills can take considerable time.
Setup Costs. Today’s big data tools rely on open source technology, which dramatically reduces software costs, but enterprises still face significant expenses related to staffing, hardware, maintenance and related services. It’s not uncommon for big data analytics initiatives to run significantly over budget and to take more time to deploy than IT managers had originally anticipated. Storage space to house the data, networking bandwidth to transfer it to and from analytics systems, and compute resources to perform those analytics are all expensive to purchase and maintain. Some organizations can offset this problem by using cloud-based analytics, but that usually doesn’t eliminate the infrastructure problems entirely.
Compliance. Compliance is defined simply as complying with government regulations. Much of the information included in companies’ big data stores are sensitive or personal, and that means the firm may need to ensure that they are meeting industry standards or government requirements when handling and storing the data.
In the Syncsort survey, data governance, including compliance, was the third most significant barrier to working with big data. In fact, when respondents were asked to rank big data challenges on a scale from 1 (most significant) to 5 (least significant), this disadvantage of big data got more 1s than other challenges.